Are you curious about the fluoride content in bottled water? Well, you’re about to find out! This article explores whether bottled water contains fluoride, a mineral that has been hailed for its dental benefits. So, if you’ve been wondering if your favorite bottled water brand is giving your pearly whites a boost, keep reading to discover the answer!
This image is property of cdn.newsapi.com.au.
What is fluoride?
Definition of fluoride
Fluoride is a naturally occurring mineral that is found in various sources such as rocks, soil, water, and plants. It is known for its ability to strengthen tooth enamel and prevent tooth decay. Fluoride is commonly added to dental products, such as toothpaste and mouthwash, as well as to public water supplies in some countries.
Benefits of fluoride
Fluoride offers several benefits to dental health. When fluoride is present in the mouth, it is absorbed by tooth enamel, which helps to strengthen and remineralize the teeth. This makes them more resistant to acid erosion and decay caused by plaque bacteria and sugary foods. Fluoride also helps to inhibit the production of acids by bacteria in the mouth, reducing the likelihood of cavity formation. Additionally, fluoride can reverse early stages of tooth decay by repairing damaged enamel through remineralization.
Potential risks of fluoride
While fluoride is generally considered safe, excessive intake can lead to potential risks. Dental fluorosis is a common side effect of excessive fluoride consumption during tooth development. It manifests as staining and pitting of the teeth, although it is usually mild and cosmetic in nature. Ingesting high levels of fluoride over a long period of time can also cause skeletal fluorosis, a condition in which fluoride accumulates in the bones and joints, leading to pain and stiffness. However, it’s important to note that optimal fluoride levels and safe exposure limits have been established to mitigate these risks.
Sources of fluoride
Natural sources of fluoride
Fluoride occurs naturally in water sources, such as lakes, rivers, and underground aquifers. It can also be found in certain foods, including fish, tea leaves, and some fruits and vegetables. The fluoride concentration in natural water sources varies depending on the geological composition of the area. In areas where the water naturally contains optimal levels of fluoride, it provides a natural means of obtaining this mineral and benefiting dental health.
Artificial sources of fluoride
Apart from natural sources, fluoride is also added to dental hygiene products, such as toothpaste and mouthwash. This allows individuals to directly apply fluoride to their teeth and gums, enhancing its protective effects against tooth decay. Additionally, some countries have implemented water fluoridation programs, where fluoride is added to public water supplies to ensure consistent access to this mineral for the population.
Fluoride in drinking water
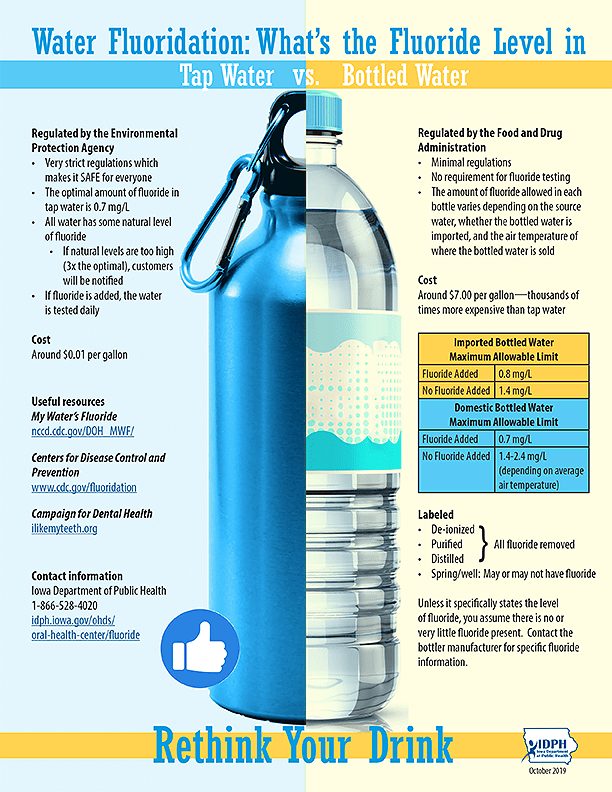
Fluoride levels in drinking water can vary depending on whether the water source is treated or untreated. In areas where water fluoridation is practiced, the fluoride concentration is carefully regulated to meet recommended levels for optimal dental health. The specific fluoride content in tap water may vary depending on local regulations and water treatment practices. It’s important to note that not all areas practice water fluoridation, and in such cases, individuals may obtain fluoride from other sources like dental products or dietary intake.
Regulations on fluoridation
Fluoride content regulations in tap water
The regulation of fluoride content in tap water differs from country to country. In regions where water fluoridation is practiced, guidelines are set to ensure that the fluoride concentration is within optimal levels for dental health. Regulatory bodies establish these standards based on scientific research and ongoing monitoring to maintain the balance between the benefits and potential risks of fluoridation. It’s important for public water supplies to meet these regulations and provide safe and consistent fluoride levels for the population.
Fluoridation policies in different countries
Fluoridation policies vary across countries and are influenced by a range of factors, including local dental health data, cultural beliefs, and public acceptance. Some countries, such as the United States, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand, have widespread water fluoridation programs that aim to improve dental health on a national level. Conversely, other countries have limited or no water fluoridation programs, relying on alternative methods, such as fluoride supplementation through dental products and education on proper oral hygiene practices.
Bottled water manufacturing process
Water sources for bottled water
Bottled water manufacturers obtain their water from various sources, including natural springs, wells, and municipal water supplies. The specific water source is often indicated on the bottle label. Natural spring water comes from underground sources that are typically protected and have minimal human influence. Well water is sourced from private wells or boreholes. Municipal water, on the other hand, is obtained from public water supplies, which may have undergone treatment and filtration prior to bottling.
Water purification methods
To ensure the safety and quality of bottled water, manufacturers employ purification methods that remove impurities and potential contaminants. Common purification methods include filtration, disinfection (e.g., UV light treatment or chlorination), and reverse osmosis. These processes help to eliminate bacteria, viruses, chemicals, and other substances that may be present in the water. By purifying the water, bottled water manufacturers aim to provide a clean and safe product for consumption.
Additives and treatments in bottled water
Some bottled waters may contain additives or undergo specific treatments to enhance taste, shelf life, or other qualities. For example, mineral water often contains naturally occurring minerals, such as calcium and magnesium, which can contribute to the flavor profile and provide additional health benefits. Some brands may also add carbonation to their water to create sparkling water. However, it’s important to note that not all bottled water undergoes such treatments, and plain purified water without additives is also widely available.


This image is property of truthaboutfluoride.com.
Fluoride in bottled water
Fluoride levels in bottled water
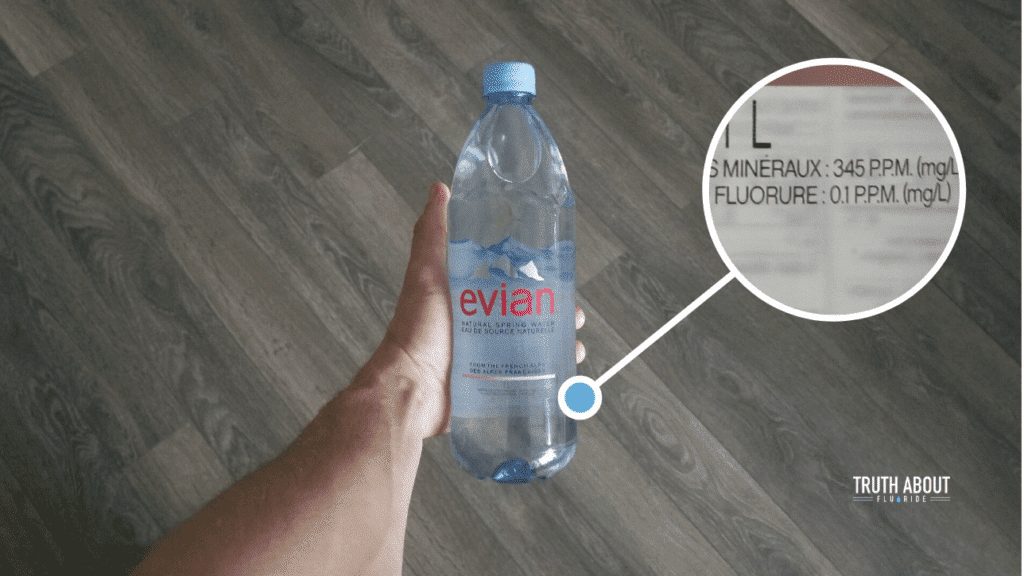
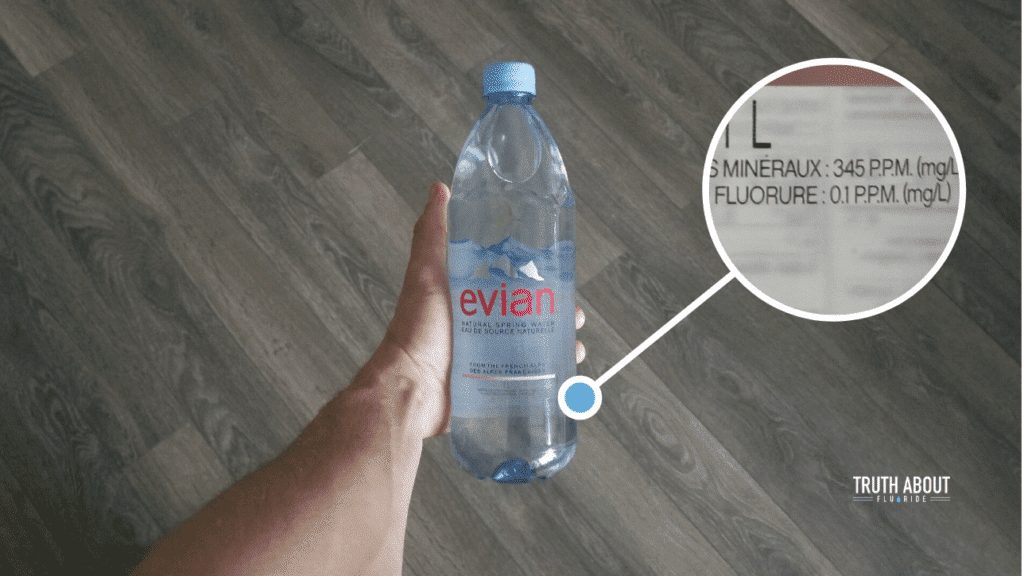
The fluoride content in bottled water can vary depending on the water source and manufacturing process. Natural spring waters may naturally contain fluoride, while purified waters may have had their fluoride content reduced or removed through filtration or other purification methods. The specific fluoride levels in bottled water can be influenced by regional regulations and the manufacturer’s own standards.
Types of bottled water containing fluoride
Some brands of bottled water market themselves as containing fluoride, aiming to provide an alternative source of this mineral for individuals who do not consume fluoridated tap water. These bottled waters may contain natural fluoride that originates from the water source. Additionally, some brands may add fluoride to the water during the manufacturing process to ensure a consistent fluoride content.
Labeling requirements for fluoride content
In many countries, including the United States, it is mandatory for bottled water labels to disclose the fluoride content if it exceeds a certain threshold. This allows consumers to make informed choices about the fluoride content in the water they purchase. The labeling requirements may also specify the acceptable range of fluoride concentration, helping individuals who desire fluoride intake to select appropriate brands.
Pros of fluoride in bottled water
Contribution to dental health
For individuals living in areas without fluoridated tap water, bottled water containing fluoride can serve as an additional means to obtain this mineral and contribute to dental health. Fluoride has been shown to be effective in preventing tooth decay, and its presence in bottled water can help promote oral hygiene and reduce the risk of developing dental cavities, especially when consumed regularly.
Accessibility for areas without fluoridated tap water
In regions where water fluoridation is not commonly practiced or available, access to fluoride may be limited. Bottled water containing fluoride provides an accessible alternative for individuals in such areas. By making fluoride readily available in bottled form, individuals who do not have access to fluoridated tap water can still obtain this essential mineral and experience its dental health benefits.


This image is property of waterfilterguru.com.
Cons of fluoride in bottled water
Cost implications
Fluoridated bottled water may come at a higher price point compared to non-fluoridated alternatives. The additional costs associated with sourcing, manufacturing, and labeling fluoride-containing bottled water can contribute to an increase in its retail price. This cost difference may be a factor to consider for individuals who are on a tight budget or prefer more affordable options.
Environmental impact of plastic bottle waste
One of the environmental concerns associated with bottled water is the production and disposal of plastic bottles. Bottled water consumption contributes to plastic waste, which has negative implications for the environment. The manufacturing and transportation of plastic bottles require energy and resources, and improper disposal can lead to pollution of land and water sources. Thus, the potential environmental impact should be considered when deciding between bottled water options.
Debates and controversies
Opposing views on fluoridation
The practice of water fluoridation has been a subject of debate and controversy. Some groups and individuals express concerns regarding the potential risks and safety of water fluoridation. These concerns range from potential adverse health effects to personal freedom to choose the level of fluoride intake. However, the World Health Organization and many dental and public health organizations support water fluoridation as a safe and effective measure to improve dental health.
Scientific studies and findings
Numerous scientific studies have been conducted to evaluate the benefits and risks of fluoride. Research consistently supports the effectiveness of fluoride in preventing tooth decay when used appropriately. The safety of water fluoridation has also been extensively studied, with the consensus being that fluoridation at recommended levels does not pose significant health risks. Scientific findings provide valuable evidence to inform regulations and policies on water fluoridation.
Public opinion and concerns
Public opinion on water fluoridation varies, with some individuals supporting and appreciating its benefits, while others express concerns or opposition. Public opinion may be influenced by personal beliefs, cultural factors, misinformation, or individual experiences. It is important for authorities and health professionals to engage with the public, provide accurate information, and address concerns to foster understanding and promote evidence-based decision making.


This image is property of truthaboutfluoride.com.
Labeling of fluoride in bottled water
Regulatory requirements for labeling
Regulatory bodies in different countries have specific requirements for labeling the fluoride content in bottled water. These regulations ensure transparency and enable consumers to make informed choices about their fluoride intake. The labeling requirements may include the mandatory disclosure of the fluoride content, instructions for use, and warnings, if applicable. Compliance with labeling regulations helps ensure that consumers have access to accurate information about the fluoride content in bottled water.
Interpreting fluoride content on labels
Understanding how to interpret the fluoride content mentioned on bottled water labels is crucial for individuals who seek to monitor their fluoride intake. The fluoride concentration is typically expressed in parts per million (ppm). It’s important to note that different bottled water brands may have varying fluoride levels, so it’s advisable to read the labels carefully and choose a brand that aligns with an individual’s desired fluoride intake.
Misleading claims and marketing tactics
In the competitive bottled water market, some brands may employ marketing tactics that can potentially mislead consumers. It’s essential for individuals to be aware of potential misleading claims related to fluoride content. Reading the label and cross-referencing information with reliable sources can help consumers make informed decisions. Staying vigilant and critically evaluating promotional messages ensures that consumers obtain accurate information about the fluoride content in bottled water.
Consumer choices and considerations
Factors to consider when choosing bottled water
When selecting bottled water, individuals can consider various factors, including their local water fluoride levels, personal dental health needs, and preferences. If tap water is fluoridated in the area, individuals may opt for non-fluoridated bottled water if they prefer to control their fluoride intake. On the other hand, individuals residing in non-fluoridated areas or desiring additional fluoride intake may choose bottled water containing fluoride. Additionally, taste preferences, cost, and environmental impact can also influence consumer choices.
Alternatives for fluoride intake
For individuals seeking alternatives for fluoride intake, dental hygiene products such as fluoride toothpaste and mouthwash can be effective options. These products provide a controlled and targeted delivery of fluoride to the teeth and gums, promoting dental health. However, it’s important to follow the instructions provided by dental professionals and use these products appropriately to maximize their benefits.
Guidelines for children and specific health conditions
Children have specific dental health needs, and fluoride plays a crucial role in their oral development. Parents should consult with pediatric dentists or healthcare professionals to ensure appropriate fluoride intake for their children. Additionally, individuals with specific health conditions or on medications that may interact with fluoride should seek guidance from healthcare professionals to determine the most suitable fluoride intake method.
In conclusion, fluoride is a mineral that offers various benefits to dental health. While it can be obtained from natural sources and tap water, bottled water can also serve as a source of fluoride. The fluoride content in bottled water varies depending on the water source and manufacturing process. Bottled water containing fluoride can contribute to dental health, especially in areas without fluoridated tap water. However, there are considerations such as cost implications and environmental impact that individuals should weigh when choosing between different bottled water options. Understanding the regulations, scientific research, and labeling requirements can help consumers make informed decisions about their fluoride intake. Ultimately, the choice of fluoride intake, whether from tap water, bottled water, or dental hygiene products, should align with individual preferences, dental health needs, and local considerations.

This image is property of ismile.idph.iowa.gov.





